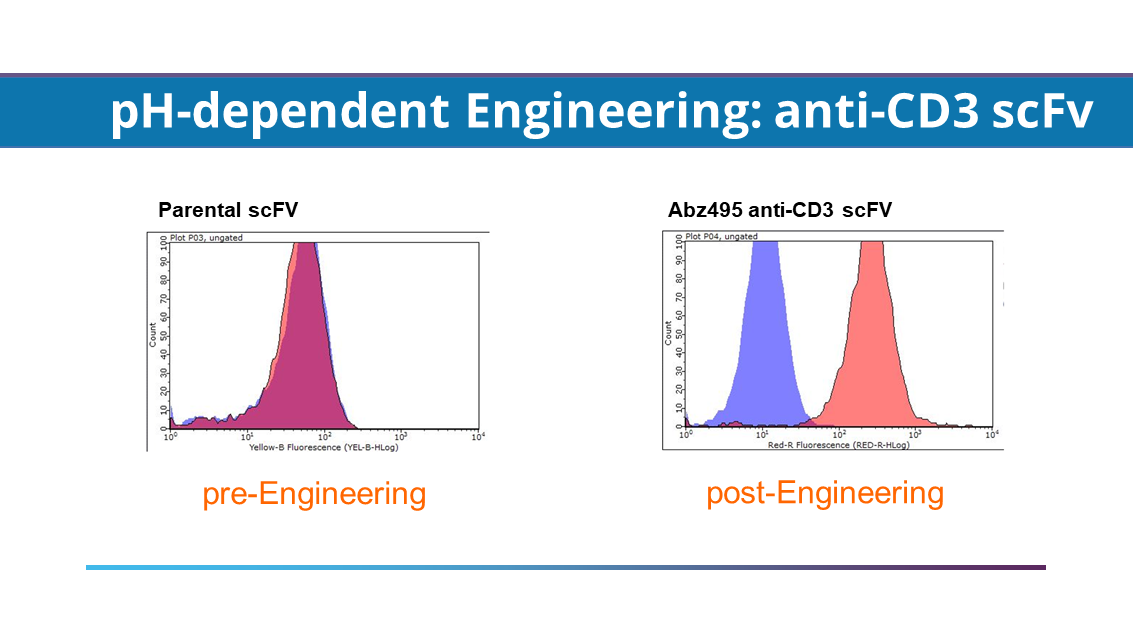
Abz495: pH-Dependent Anti-CD3 T-cell Engager Available for Licensing
For scFv-based modulars, pH-dependent anti-CD3 scFv and human/Cyno cross-reactive, anti-CD3 scFv are two modulars that can be used as an arm in T-cell-engaging bispecific antibodies. Abz495 is a pH-dependent anti-CD3 scFv that binds strongly to human CD3 in the acidic tumor microenvironment, but has negligent binding in normal tissues.
Expression of tumor antigens on normal tissues can lead to “on-target, off-tumor” activation of T-cells outside of tumors. Cytotoxic T-cell activity to normal cells can cause life-threatening side effects that limit the dose escalation required to achieve therapeutic efficacy against solid tumors. pH-dependent Abz495 will improve the safety profile of your therapeutic by limiting its activity to the tumor microenvironment and increase its therapeutic efficacy.
Anti-human and cynomolgus CD3 scFV are useful for development of T-cell engagers that can be validated in non-human primates.
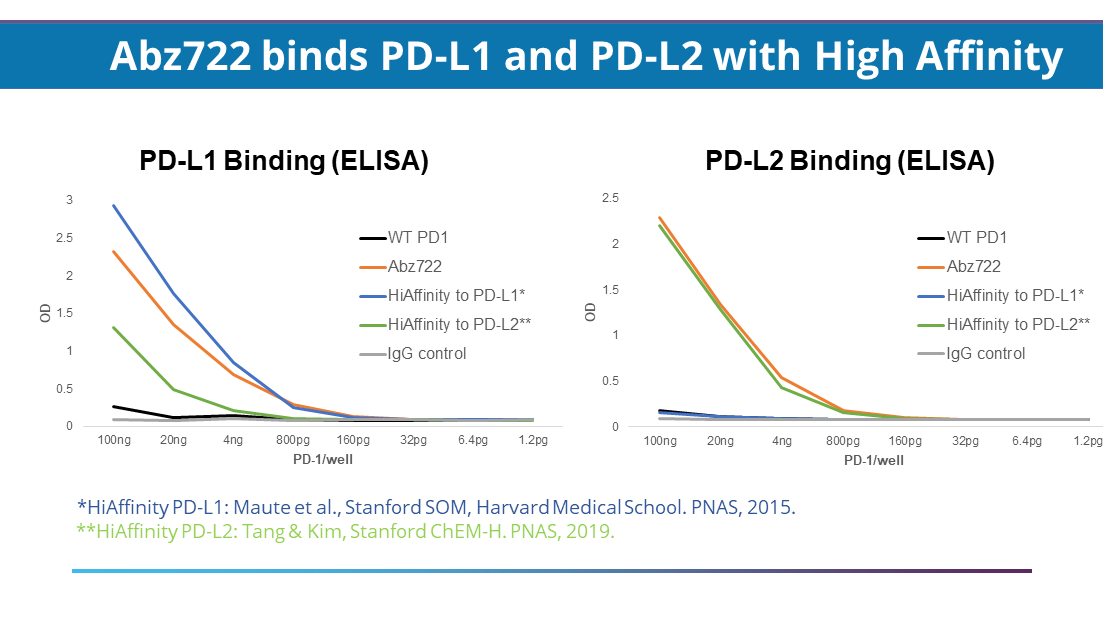
Dual ligand-binding PD-1, Abz722: Available for Licensing or Co-development
Using our protein evolution platforms, we have engineered a set of immune checkpoint receptors with high affinity to their ligands. These soluble immune checkpoint inhibitors with high target affinity can be used to disrupt the immune checkpoint pathway to release the immune system to fight cancer. Abz722 is an engineered PD1 receptor that has sub-nanomolar affinity to both PD-L1 and PD-L2 ligands, which are both highly expressed on cancer cells.
Abzyme has the following preclinical VHH-based antibody assets for the development of novel cross-linking therapies:
- Anti-TIGIT VHH
- Anti-VEGF VHH
- Anti-ANGPTL4 VHH
- Anti-CD147 VHH
- Anti-BCMA VHH
- Anti-CD19 VHH
- Anti-CD22 VHH
- Anti-CD33 VHH
Abzyme Therapeutics has developed a number of modular therapeutic candidates for immuno-oncology. These assets are available for out-licensing or co-development. These biologic candidates can be further developed as stand-alone therapeutics or a component of multi-specific antibodies. Most of our modular candidates are single-domain VHH antibodies that are ideal for constructing novel immunotherapies for cancer. Their small size and single-chain structure does not require the correct folding environment for activity that standard antibodies and scFvs do. Therefore, VHH domains can readily be used to construct bi- and even multi-specific immunotherapies and quickly recruited for use in CAR-T and CAR-NK therapies. Besides VHH-based antibodies, Abzyme has engineered other modular biologics applicable for cancer treatment. Some modulars are based on scFv. Other modulars are engineered receptors.